Content Summary
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of human life, and its importance cannot be overstated. Far from being a passive state, sleep plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, cognitive function, and emotional health.
The enigmatic world of dreams intrigues and captivates us as we slumber. This article dives into the significance of sleep, the mysteries behind why we sleep and dream, the consequences of sleep deprivation, the stages of healthy sleep patterns, and the numerous benefits of good sleep, including its potential impact on longevity and well-being.
Why We Sleep and Dream
The exact reasons behind why we sleep and dream remain the subject of ongoing research and fascination for scientists and researchers. While we do not have all the answers, several theories shed light on the importance of these fundamental phenomena.
Restoration and Repair: Sleep allows the body and brain to engage in essential repair processes, such as cellular regeneration and the consolidation of memories, aiding in overall physical and mental restoration.
Memory Consolidation: During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates the information and experiences acquired throughout the day, reinforcing learning and enhancing cognitive performance.
Energy Conservation: Sleep is an energy-saving state that allows the body to replenish its energy reserves, ensuring optimal functioning during wakeful hours.
Brain Cleansing: Sleep may facilitate the removal of toxic waste products from the brain, including beta-amyloid, a protein associated with Alzheimer's disease, helping to maintain brain health.



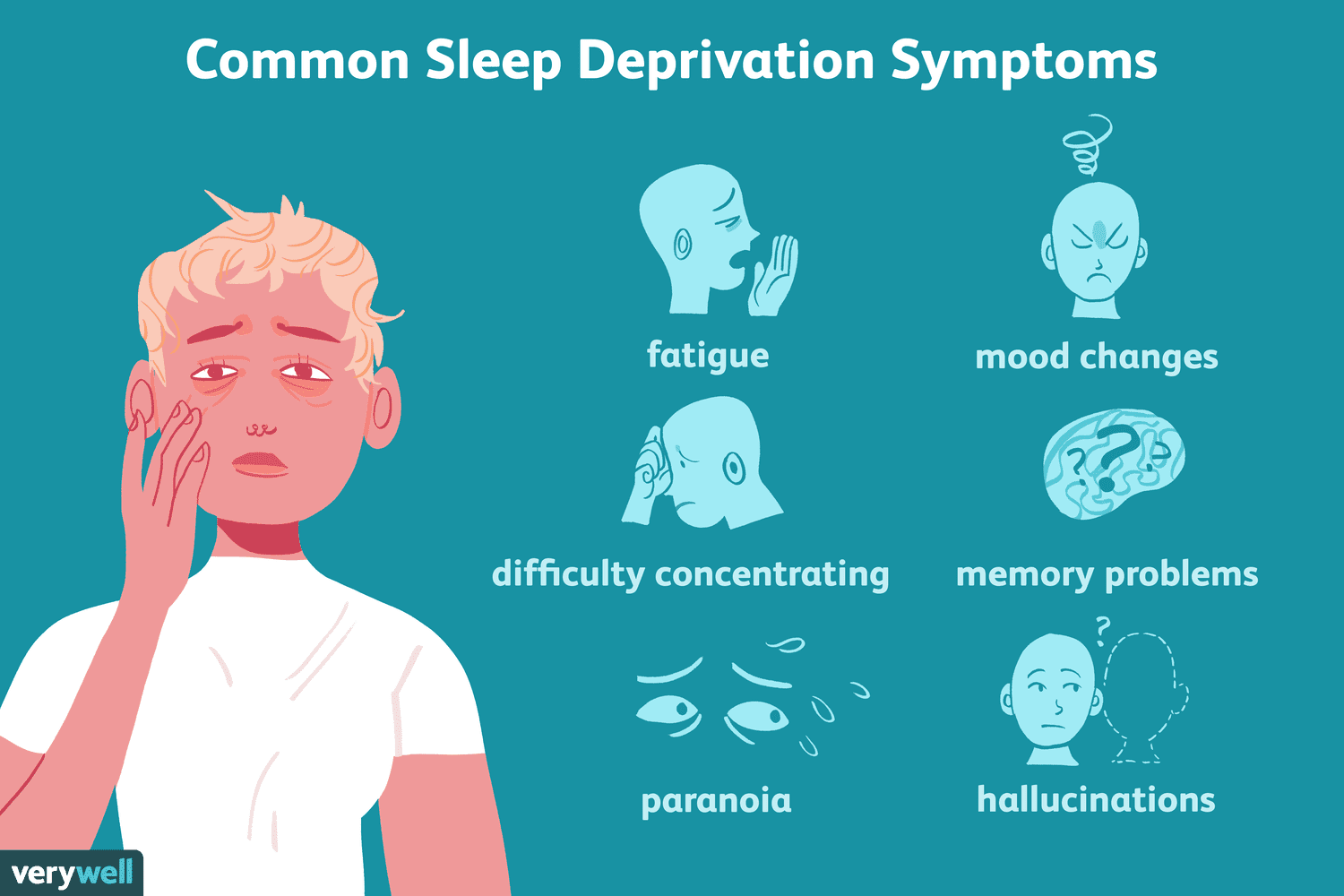
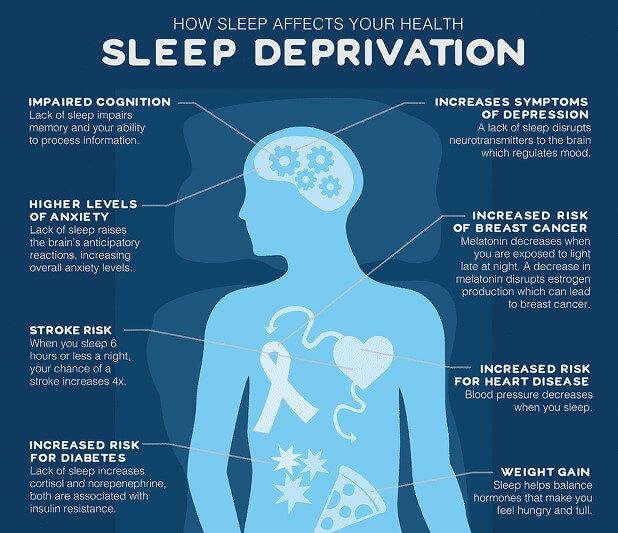
Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
The consequences of sleep deprivation extend beyond mere fatigue and grogginess. Chronic sleep deprivation can have severe repercussions on both physical and mental health:
Impaired Cognitive Function: Lack of sleep hinders attention, concentration, problem-solving abilities, and memory recall.
Emotional Disturbances: Sleep deprivation can lead to increased irritability, mood swings, and heightened emotional sensitivity.
Weakened Immune System: Inadequate sleep weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Cardiovascular Issues: Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.

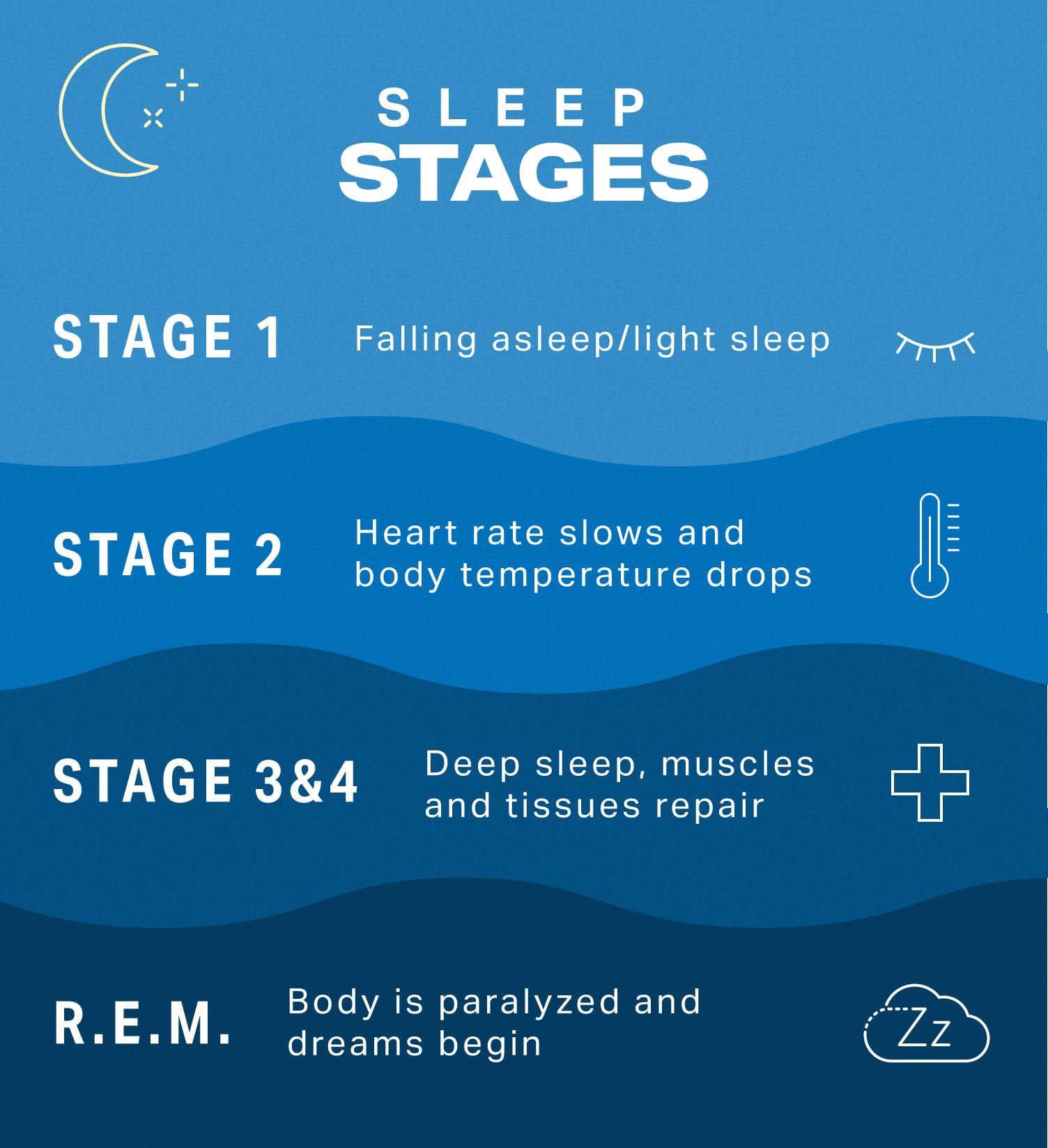
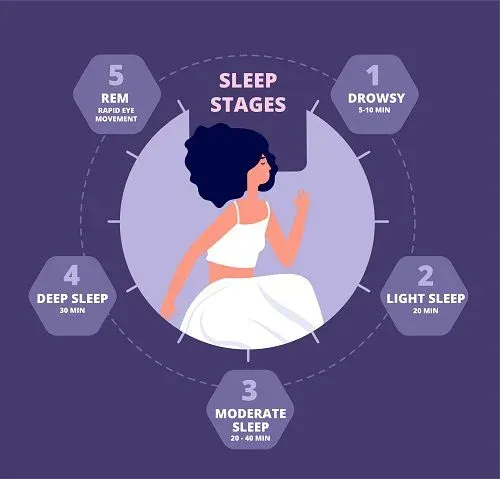
The Stages of Healthy Sleep Patterns
Healthy sleep is characterized by distinct stages that form a sleep cycle. These stages are:
Non-REM Sleep Stage 1: The transition from wakefulness to sleep, lasting only a few minutes.
Non-REM Sleep Stage 2: A period of light sleep where brain activity slows, and the body prepares for deeper sleep.
Non-REM Sleep Stage 3: Also known as deep sleep, crucial for physical restoration and renewal.
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep: The stage where dreaming occurs, associated with memory consolidation and emotional processing.
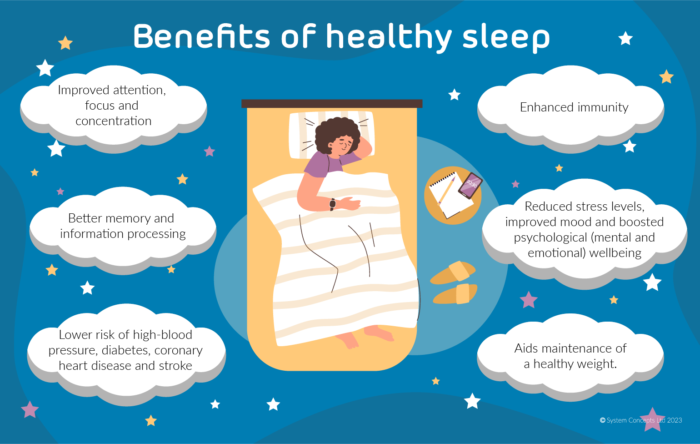
The Benefits of Good Sleep
Enhanced Cognitive Function: Quality sleep bolsters cognitive abilities, improving focus, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Emotional Well-being: Adequate sleep promotes emotional resilience, reducing the risk of anxiety and depression.
Physical Health: Sound sleep contributes to a stronger immune system, cardiovascular health, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Weight Management: Sufficient sleep plays a role in appetite regulation, aiding in weight maintenance.


Sleep Longevity and Well-being
Emerging research suggests that good sleep habits may influence longevity and overall well-being. Studies have linked consistent, restorative sleep with a lower risk of chronic health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive decline. Moreover, quality sleep is associated with improved mental health, reduced stress, and a greater sense of well-being.
Most FAQs About the Importance of Sleep:
How Much Sleep Does a Middle Age Person Need?
The amount of sleep needed can vary from person to person, but generally, middle-aged adults, like adults of other age groups, require 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night.
This range is considered optimal for most middle-aged individuals to maintain their physical health, cognitive function, and emotional well-being.
As we age, our sleep patterns and needs can change, and some individuals may find that they need slightly less or slightly more sleep than the average recommended range. Factors such as lifestyle, genetics, overall health, and daily activity levels can also influence an individual's sleep requirements.
It's essential for middle-aged adults to pay attention to their own bodies and sleep quality to determine what works best for them. If you consistently feel well-rested, alert, and energized during the day, you are likely getting the right amount of sleep for your needs.
However, if you regularly experience daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, or mood disturbances, it might indicate that you need to adjust your sleep duration or improve your sleep quality.
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and maintaining a sleep-conducive environment can all contribute to getting the right amount of restful sleep for middle-aged individuals and promoting overall health and well-being.
If you have concerns about your sleep patterns or are experiencing persistent sleep difficulties, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist for personalized guidance and recommendations.
How do Caffeine and Alcohol Affect Sleep?
Caffeine and alcohol are two substances that can significantly impact sleep patterns and overall sleep quality.
Caffeine:
Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain medications. Its primary effect is to block the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and drowsiness. As a result, caffeine increases alertness and temporarily reduces feelings of fatigue.
Effects on Sleep:
Delayed Sleep Onset: Consuming caffeine, especially in the afternoon or evening, can interfere with the ability to fall asleep. The stimulating effects of caffeine can disrupt the natural process of winding down before bedtime.
Reduced Sleep Duration: Caffeine can also lead to shorter sleep durations, as it may cause awakenings during the night or prompt individuals to wake up earlier than desired.
Shallow Sleep: Even when people manage to fall asleep after consuming caffeine, their sleep may be lighter and less restorative, leading to a decreased quality of sleep overall.
Recommendations:
To avoid sleep disruptions caused by caffeine, it's advisable to limit its consumption, especially in the afternoon and evening. Individuals who are sensitive to caffeine should consider avoiding it altogether in the hours leading up to bedtime. Opt for decaffeinated beverages or herbal teas if you still crave a warm drink in the evening.
Alcohol:
Alcohol is a depressant that can initially induce drowsiness and relaxation. It may help some people fall asleep faster due to its sedative effects. However, its impact on sleep quality is complex and can be detrimental.
Effects on Sleep:
Disrupted Sleep Architecture: Alcohol consumption can disrupt the natural sleep architecture, leading to fragmented sleep patterns and a reduction in deep, restorative sleep stages.
Increased Nighttime Awakenings: While alcohol might facilitate the onset of sleep, it often results in increased awakenings during the night, leading to less restful sleep overall.
Sleep Disordered Breathing: Alcohol can relax the muscles in the upper airway, leading to snoring and an increased risk of sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep.
Recommendations:
If you choose to consume alcohol, it's best to do so in moderation and avoid drinking close to bedtime. Allow sufficient time for the body to metabolize the alcohol before going to sleep to reduce its disruptive effects on sleep.
Both caffeine and alcohol can negatively impact sleep, affecting the duration and quality of rest. To promote better sleep, it's essential to be mindful of the timing and quantity of caffeine and alcohol consumption.
Maintaining a healthy sleep routine, including consistent sleep and wake times, a relaxing bedtime routine, and a sleep-conducive environment, can also help ensure more restful and restorative sleep.
How Sleep Apnea Affects Sleep Quality?
Sleep apnea significantly affects sleep quality and can have negative consequences on overall health and well-being. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, can last for a few seconds to minutes and occur multiple times throughout the night.
There are two main types of sleep apnea:
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common form, OSA occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the airway.
Central Sleep Apnea: This less common form is caused by a failure of the brain to send the appropriate signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Effects of Sleep Apnea on Sleep:
Fragmented Sleep: The frequent awakenings caused by apneas disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to fragmented and shallow sleep.
Reduced Sleep Quality: Sleep apnea can result in a reduction of deep, restorative sleep stages, such as REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and slow-wave sleep.
Daytime Sleepiness: The constant sleep disruptions can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, impacting daytime functioning and cognitive abilities.
Loud Snoring: Loud and persistent snoring is a common symptom of sleep apnea, which can also disturb the sleep of bed partners.
Gasping and Choking: People with sleep apnea may experience sudden awakenings accompanied by gasping or choking as they struggle to catch their breath.
Consequences of Untreated Sleep Apnea:
If left untreated, sleep apnea can have significant negative effects on an individual's health and well-being:
Increased Cardiovascular Risk: Sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and irregular heart rhythms.
Daytime Impairment: Excessive daytime sleepiness can impair cognitive function, leading to decreased concentration, memory problems, and decreased productivity.
Mood Disturbances: Sleep apnea is linked to mood disorders such as depression and irritability.
Motor Vehicle Accidents: The impaired daytime alertness can increase the risk of motor vehicle accidents due to drowsy driving.
Treatment for Sleep Apnea:
Fortunately, sleep apnea is treatable. The most common and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, where a machine delivers a constant flow of air to keep the airway open during sleep. Other treatment options may include oral appliances, lifestyle changes, weight management, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that negatively impacts sleep quality, leading to daytime sleepiness and various health consequences. Seeking timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment for sleep apnea is crucial to improve sleep quality, enhance overall well-being, and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have sleep apnea, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist for proper evaluation and guidance.
How Long Can a Human Live Without Sleep?
The exact duration a person can survive without sleep varies and depends on several factors, including individual differences, health status, age, and other environmental factors.
However, complete sleep deprivation is not sustainable for an extended period, and its effects on the body and mind become increasingly severe as time progresses.
The world record for voluntary sleep deprivation stands at approximately 11 days, achieved by Randy Gardner in 1965 as part of a high school science fair project. During this period, he experienced significant physical and psychological symptoms, including hallucinations, mood swings, cognitive impairment, and memory deficits.
Generally, the lack of sleep can lead to severe consequences after just a few days: Cognitive Impairment Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive functions, including attention, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Emotional Disturbances: Prolonged sleep deprivation can lead to heightened emotional sensitivity, irritability, and mood swings.
Hallucinations and Delusions: Individuals experiencing extended sleep deprivation may begin to have hallucinations and delusions.
Weakened Immune System: Lack of sleep suppresses the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Increased Risk of Accidents: Sleep-deprived individuals are more prone to accidents and errors, especially when driving or operating heavy machinery.
It's important to note that prolonged sleep deprivation is not recommended, as it can have serious health implications and may be life-threatening. The body requires sleep for proper physical and mental functioning, and chronic sleep deprivation can lead to severe health problems.
If you or someone you know is experiencing difficulty sleeping or signs of chronic sleep deprivation, it's essential to seek medical advice to address the underlying causes and improve sleep patterns. Prioritizing regular, restful sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a sleep disorder characterized by a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It occurs during the transition between sleep stages, particularly during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep or just before entering REM sleep. REM sleep is a stage of sleep associated with vivid dreaming and rapid eye movements.
During sleep paralysis, the brain is awake and conscious, but the body remains in a state of muscle atonia, which is a natural mechanism that prevents us from acting out our dreams during REM sleep.
This temporary paralysis typically ensures that we remain still and safe while dreaming. However, in cases of sleep paralysis, the transition from REM sleep to wakefulness is disrupted, and the individual becomes aware of their surroundings while still being unable to move or speak.
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis:
Inability to move: The person is unable to move their limbs, despite being fully aware of their surroundings.
Inability to speak: During sleep paralysis, speech muscles may be affected, leading to the inability to vocalize or call for help.
Hallucinations: Individuals experiencing sleep paralysis may also report vivid and sometimes frightening hallucinations, often described as shadowy figures or presence in the room.
Feeling of pressure on the chest: Some people may feel a sensation of pressure on their chest, making breathing difficult.
Sleep paralysis episodes can be brief, lasting for a few seconds to a few minutes, but they can be distressing and frightening for those experiencing them. After the episode, individuals typically regain their ability to move and speak without any lingering effects.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis:
The exact causes of sleep paralysis are not fully understood, but certain factors may contribute to its occurrence:
Disrupted Sleep Patterns: Sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, and insomnia can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders like narcolepsy, a condition characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, are associated with an increased risk of sleep paralysis.
Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can trigger sleep disturbances, potentially leading to sleep paralysis.
Sleep Position: Sleeping on the back is often linked to a higher incidence of sleep paralysis.
Treatment for Sleep Paralysis:
In most cases, sleep paralysis does not require specific treatment. However, addressing any underlying sleep disorders or improving sleep hygiene can be beneficial in reducing the frequency of episodes.
Managing stress and anxiety through relaxation techniques and stress-reduction strategies may also help. If sleep paralysis episodes are causing significant distress or disruption to daily life, consulting a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist can provide further guidance and support.
How to Improve Sleep Quality?
Improving sleep quality is essential for overall health and well-being. Here are some tips and strategies to enhance the quality of your sleep:
Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Consistency helps regulate your body's internal clock and improves the overall quality of your sleep.
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Establish a calming pre-sleep routine to signal to your body that it's time to wind down. This may include activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation exercises like deep breathing or meditation.
Make Your Bedroom Sleep-Conducive: Create a comfortable and peaceful sleep environment. Ensure that your bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Invest in a supportive mattress and pillows that suit your preferences.
Limit Exposure to Screens Before Bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Aim to avoid screens like smartphones, computers, and televisions at least an hour before bedtime.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: Both caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns. Avoid consuming them close to bedtime, and consider limiting overall intake, especially in the evening.
Get Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve sleep quality. However, try to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may be stimulating and affect your ability to fall asleep.
Manage Stress: High levels of stress and anxiety can interfere with sleep. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, or journaling.
Avoid Large Meals Before Bed: Eating a heavy meal before bedtime can lead to discomfort and indigestion, making it harder to fall asleep. Opt for a light snack if you're hungry before bed.
Limit Daytime Naps: While short daytime naps can be refreshing, excessive or late-afternoon napping can disrupt nighttime sleep. If you need to nap, keep it short (20-30 minutes) and earlier in the day.
Monitor Your Sleep Environment: Assess the comfort and ambiance of your sleep environment regularly. Address any issues that may disrupt your sleep, such as noise, temperature, or uncomfortable bedding.
Seek Help for Persistent Sleep Problems: If you continue to experience difficulties with sleep despite trying these strategies, consider seeking advice from a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist. They can help identify and address any underlying sleep disorders or issues.
Remember that improving sleep quality may take time and patience, as it involves creating healthy sleep habits and maintaining a consistent routine. Prioritizing good sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, and the benefits of restful sleep extend to all aspects of life.
Author's Choice of Self-Improving Books about Quality Sleep:



Conclusion
Sleep is a powerful ally in our pursuit of a healthy and fulfilling life. Understanding why we sleep and dream, as well as the consequences of sleep deprivation, emphasizes the importance of prioritizing our sleep habits.
Embracing healthy sleep patterns not only enhances cognitive function, emotional well-being, and physical health but may also have a positive impact on longevity and overall life satisfaction.
So, let us embrace the gift of sleep and unlock its potential to nurture our minds and bodies, ensuring a brighter and more vibrant future.
Relevant Reads>>>