Content Summary
As humans, we like to believe that our decisions and judgments are rational and objective. However, the truth is that our minds are often influenced by cognitive biases.
These biases are mental shortcuts that our brains use to process information quickly and efficiently, but they can also lead us astray. In this article, we will explore what cognitive bias is, its connection to bias in general, and practical ways to deal with it.
What is Cognitive Bias
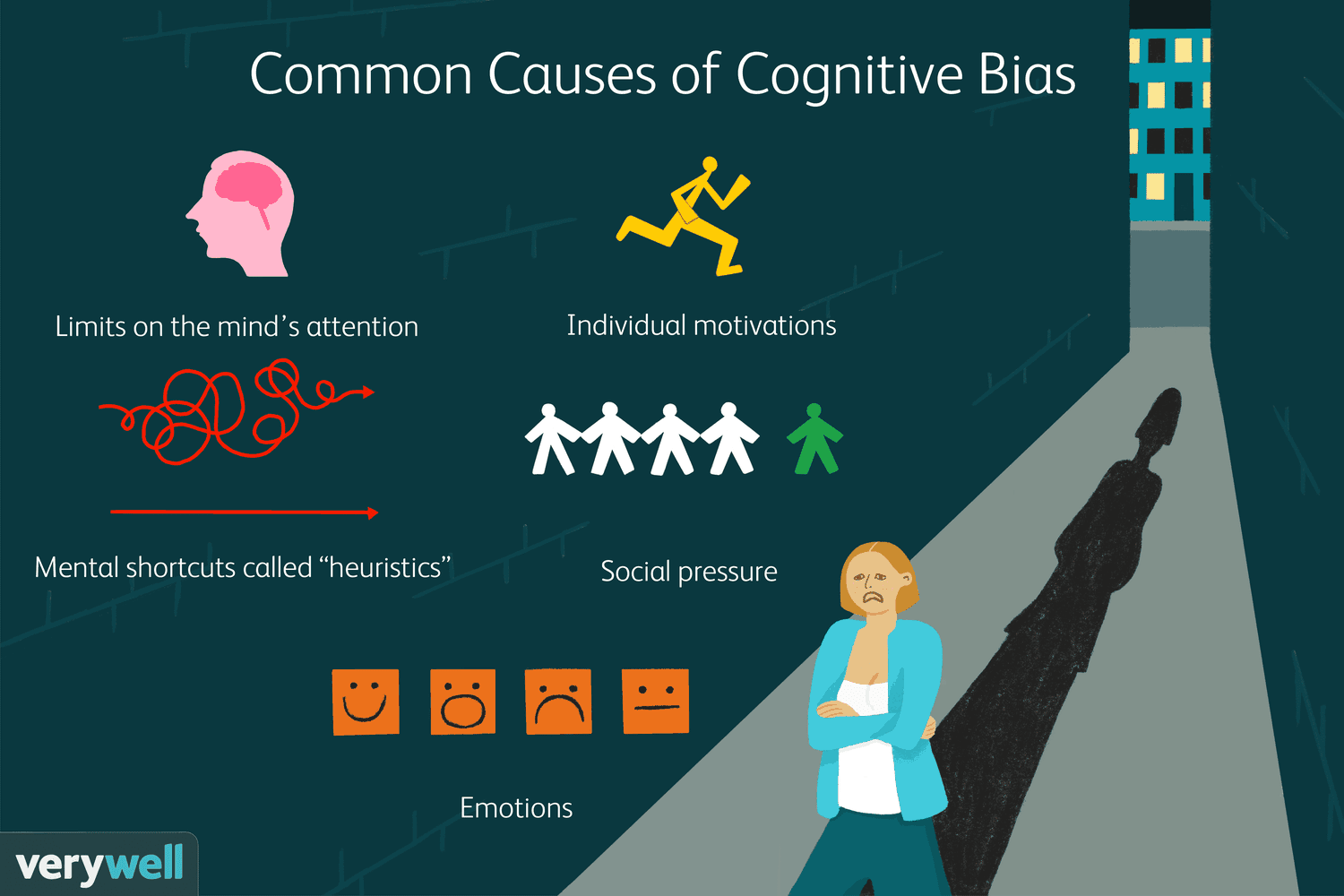
Cognitive bias is a pattern of systematic deviation from objective judgment or rationality in decision-making. It is an inherent feature of human cognition and affects individuals of all backgrounds and intelligence levels.
Our brains use cognitive biases as a way to simplify complex information, aiding us in making faster decisions in a world filled with overwhelming stimuli.
While these mental shortcuts can be beneficial in some situations, they can also lead to flawed judgments, misunderstandings, and illogical choices.
Cognitive biases can impact various aspects of our lives, including personal relationships, professional decisions, and even societal perceptions.
The Connection Between Cognitive Bias and Bias
To understand cognitive bias better, it is essential to acknowledge its connection to the broader concept of bias. Bias, in general, refers to a predisposition or preference for one thing over another. It can be conscious or unconscious and may stem from personal beliefs, cultural influences, or societal norms.
Cognitive biases are a subset of bias, specifically related to the way our minds process information. They affect how we perceive and interpret data, often leading us to make judgments based on our preexisting beliefs and assumptions. These biases can reinforce stereotypes, lead to unfair judgments, and hinder us from making well-informed and impartial decisions.
Common Types of Cognitive Bias
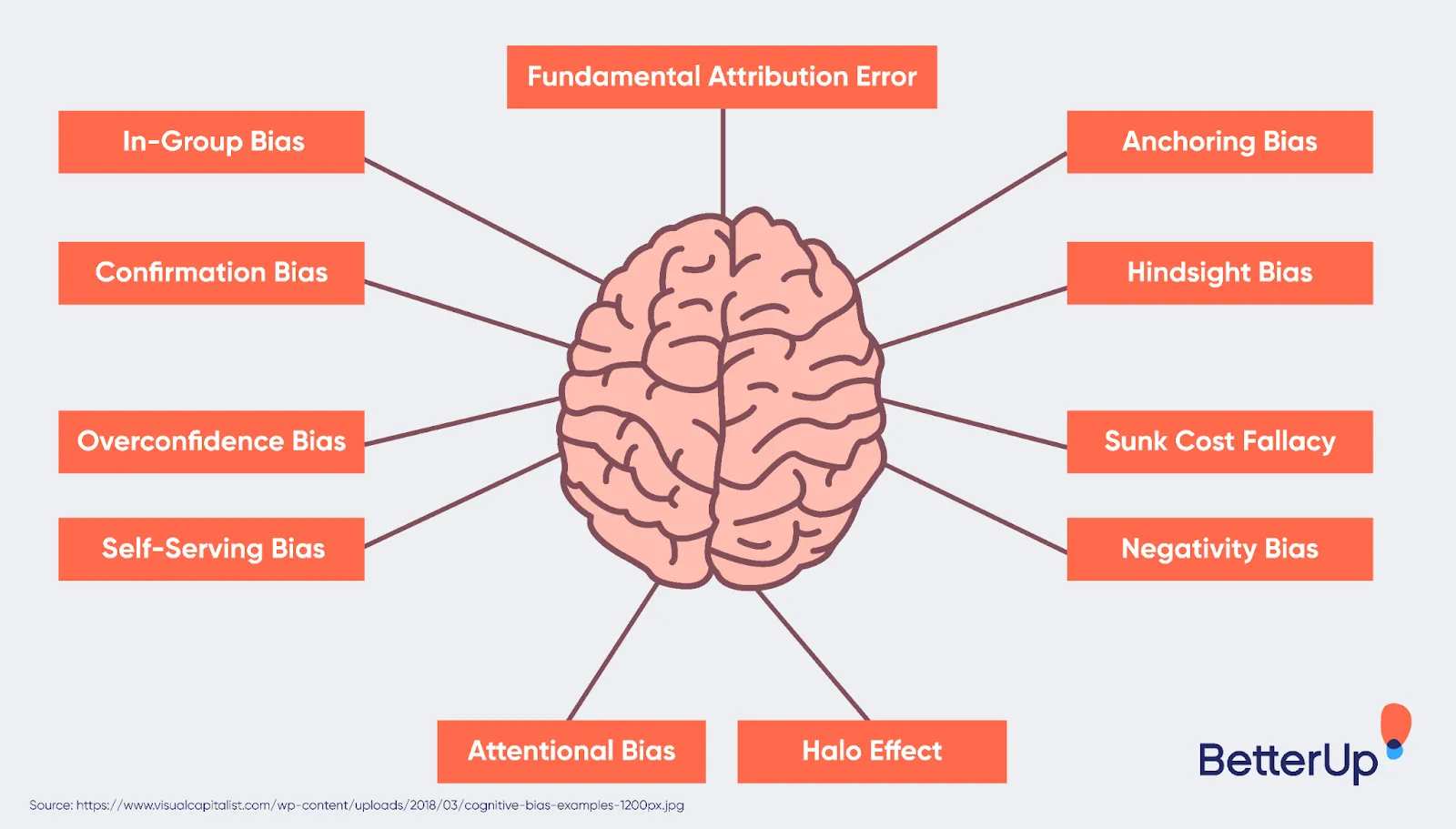
There are numerous cognitive biases, each impacting different aspects of human cognition. Some of the most common cognitive biases include:
Confirmation Bias: Tendency to seek and favor information that confirms preexisting beliefs, while ignoring or downplaying contradictory evidence.
Availability Heuristic: Relying on readily available examples or information when making decisions, often leading to overestimating the probability of rare events.
Anchoring Bias: The tendency to rely heavily on the first piece of information encountered when making judgments, even if it's irrelevant or misleading.
Halo Effect: Forming a general impression of a person based on a single positive characteristic, leading to skewed perceptions of their overall qualities.
Bandwagon Effect: Adopting certain behaviors or beliefs because others around us are doing the same, often disregarding our independent judgment.
Dealing with Cognitive Bias
Overcoming cognitive bias requires self-awareness, open-mindedness, and a willingness to challenge our own thought processes. Here are some strategies to deal with cognitive bias:
Recognize Your Biases: Reflect on your thoughts and decisions to identify patterns of bias. Acknowledging your biases is the first step toward minimizing their impact.
Seek Diverse Perspectives: Surround yourself with diverse individuals who have different backgrounds and viewpoints. Engaging in meaningful conversations with others can broaden your understanding and reduce bias.
Verify Information: Avoid making snap judgments based on limited information. Take the time to gather more data and verify facts before reaching conclusions.
Encourage Feedback: Welcome constructive criticism from others. This can help you identify blind spots and challenge your assumptions.
Think Systematically: Engage in deliberate and analytical thinking processes. Question your own judgments and consider alternative explanations.
12 Cognitive Biases Explained
Author's Choice of Tools for Self-Help Recognizing and Eliminate the Negative Influence:



Conclusion
Cognitive biases are a natural aspect of human cognition, but they can lead us astray if left unchecked. By understanding what cognitive bias is and recognizing its influence on our decisions, we can take proactive steps to mitigate its impact.
By embracing open-mindedness, seeking diverse perspectives, and thinking systematically, we can navigate the intricate maze of cognitive biases and make more informed, fair, and rational judgments.
Remember, it is not about eradicating bias entirely, but about striving to be more aware and objective in our thinking processes.
Relevant Reads>>>













